

The bladder stretch reflex is a primitive spinal reflex, in which micturition is stimulated in response to stretch of the bladder wall. They are found in the bladder wall and signal the need to urinate when the bladder becomes full. In addition to the efferent nerves supplying the bladder, there are sensory (afferent) nerves that report to the brain. It innervates the external urethral sphincter, providing voluntary control over micturition. Increased signals from this nerve causes contraction of the detrusor muscle, stimulating micturition. Parasympathetic – pelvic nerve (S2-S4).It causes relaxation of the detrusor muscle, promoting urine retention. Sympathetic – hypogastric nerve (T12 – L2).Neurological control is complex, with the bladder receiving input from both the autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and somatic arms of the nervous system: However, in males the external sphincteric mechanism is more complex, as it correlates with fibers of the rectourethralis muscle and the levator ani muscle. It is skeletal muscle, and under voluntary control. External urethral sphincter – has the same structure in both sexes.It is formed by the anatomy of the bladder neck and proximal urethra. Females – thought to be a functional sphincter (i.e.It is thought to prevent seminal regurgitation during ejaculation. Male – consists of circular smooth fibres, which are under autonomic control.

There are also two muscular sphincters located in the urethra: This is very common in conditions that obstruct the urine outflow such as benign prostatic hyperplasia. The fibers of the detrusor muscle often become hypertrophic (presenting as prominent trabeculae) in order to compensate for increased workload of the bladder emptying. It receives innervation from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Its fibres are orientated in multiple directions, thus retaining structural integrity when stretched. In order to contract during micturition, the bladder wall contains specialised smooth muscle – known as detrusor muscle. The musculature of the bladder plays a key role in the storage and emptying of urine. In contrast to the rest of the internal bladder, the trigone has smooth walls (this is explained by the different embryological origin: the trigone is developed by the integration of two mesonephric ducts at the base of the bladder).įig 2 – Anatomical features of the bladder. Internally, these orifices are marked by the trigone – a triangular area located within the fundus. Urine enters the bladder through the left and right ureters, and exits via the urethra.
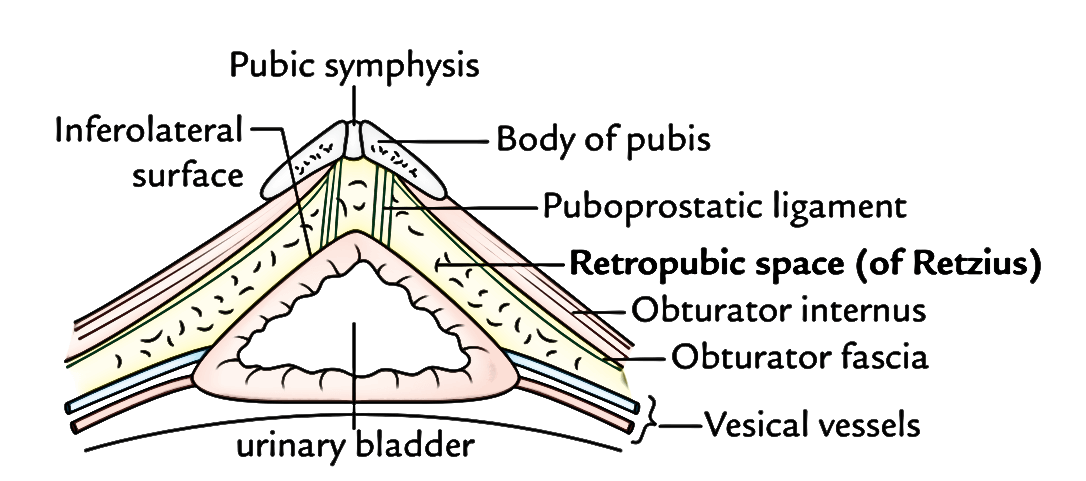

It is triangular-shaped, with the tip of the triangle pointing backwards. Fundus (or base) – located posteriorly.Body – main part of the bladder, located between the apex and the fundus.It is connected to the umbilicus by the median umbilical ligament (a remnant of the urachus). Apex – located superiorly, pointing towards the pubic symphysis.The external features of the bladder are: When full, it exhibits an oval shape, and when empty it is flattened by the overlying bowel. The appearance of the bladder varies depending on the amount of urine stored.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
